
- Rstudio source on save how to#
- Rstudio source on save code#
- Rstudio source on save license#
- Rstudio source on save download#
If needed, select comma to encode decimal points into commas. This is the default setting and you can keep it set to period for our purposes. If there are decimal points in your data, select period to use the period character for the decimal point. Other options include whitespace, tab, or a semicolon.ĭecimal. You can see this in the input file window. If we, selected no, our first row of data would contain the column names, such as Entity.Type, etc. This works well if you do not have a header, but in our case we do and we don’t want R to create a header for us. If you do not select yes to heading, R will create a default header using V’s (e.g.
Rstudio source on save license#
These include Entity.Type, License Number, ., etc. Select yes since the first row in the dataset contains the column headings. Let’s replace it with sidewalk, as shown in Figure 3.7. Here you can set your preferences for how you would like R to read in your. This will launch the Import Text Data window, see Figure 3.7. Select From CSV File… to import a CSV file that is stored on your hard drive.įigure 3.6: Navigating to your file in RStudio. To import a CSV file simply click on the import dataset button in your workspace. In RStudio the upper right quadrant is called your workspace.
Rstudio source on save download#
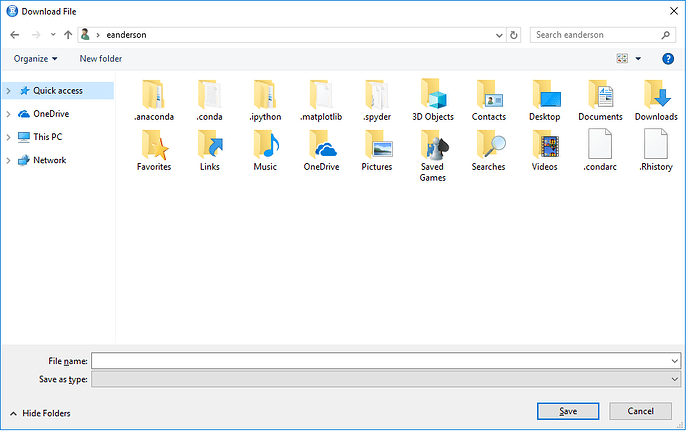
You can download the dataset from:įind the Sidewalk_Cafe.csv file that you downloaded (you can probably find it in your Downloads folder on your computer) and move it to your mydata folder on your desktop. Let’s use a file from NYC Open data on Sidewalk Cafes. 4).īefore we can import a file, we need to have a file to import. Usually, all records have an identical sequence of fields ( (“Comma Separated Values” 2018), para. A CSV file consists of any number of records, separated by line breaks of some kind each record consists of fields, separated by some other character or string, most commonly a literal comma or tab. Plain text means that the file is a sequence of characters, with no data that has to be interpreted instead, as binary numbers. This file format stores tabular data (numbers and text) in plain-text form. "CSV stands for comma-separated values or character-separated values. This means your file will have an extension. Many files you will be using in this course will be in. I would recommend you first export your file as a CSV from the program you created the file in, such as Excel. However, the cleanest and easiest way to import data is as a CSV file. In R, you can import data files that you created in Excel, MiniTab, SPSS, Stata, and many more programs. To learn which packages are installed in your version of R, type:

A package is a big collection of functions and other R objects that are all grouped together under a common name.
Rstudio source on save how to#
Finally, you will learn how to produce polished reports and publish them to the web.Īll of the functions that you’ll want to use in R come in the form of packages.
Rstudio source on save code#
In this session we’ll focus learn more about the extended packages available in R, configure our working space, learn how to import and work with a CSV file, manipulate data frames, develop proficiency in writing R scripts, and document your R code using comments.



 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
